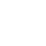
The current GRAFT block reward (the proof-of-work fee that the miners receive when they “solve” the block and successfully add it to the blockchain) today is approximately 1,420 GRFT, so every day the GRAFT circulation grows by more than 1 million (!) GRFT. Unfortunately, many miners use the high profitability of GRAFT to immediately sell their mining rewards on exchanges, which keeps bringing the price down as the demand cannot keep up with such a rapidly growing supply. Even growing demand cannot catch up to the emission rate because the project is too young.
Although the block reward is designed to decrease with every block, the current rate by which emissions are decreasing is not significant enough to counteract the overall supply increase rate from miners dumping. It will be significantly lower in, let’s say, one or two years, but the GRAFT team and supporters (including miners) cannot wait that long. We all need the economics to stabilize in the near term in order for the project to regain its footing and bring things into balance.
It is hard to anticipate these imbalances ahead of time as we’re trail blazing in a lot of respects. The only thing we can do is react quickly and adjust things whenever we see the “go off the rails” potential.
Note that ERC20 token-based projects do not have the problem described above because they don’t have a real blockchain. Their token supply remains the same (actually, it is even reduced with every exchange transaction), so they just need to make sure their demand at least remains the same in order to constantly pump the price and the market cap.
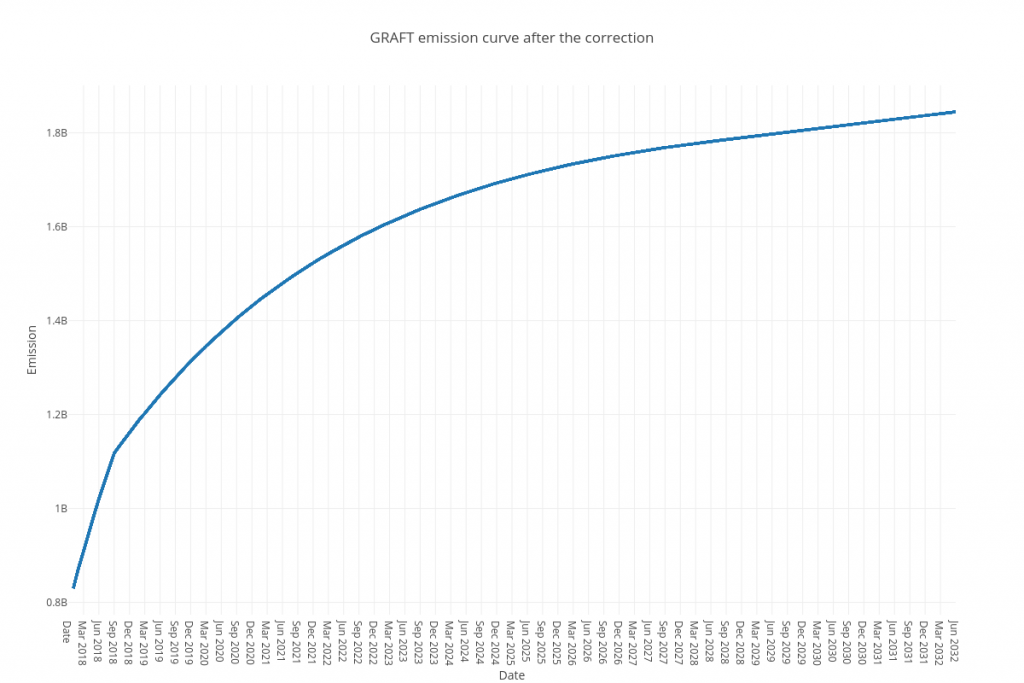
With that said, in order to rebalance the network economics, we have decided to correct the emission by reducing the block reward by 50%, so the new block reward formula will be as following:
reward = (M – A) * 2^-19 * 10^-10 / 2
Where M is max total supply and A is current supply.
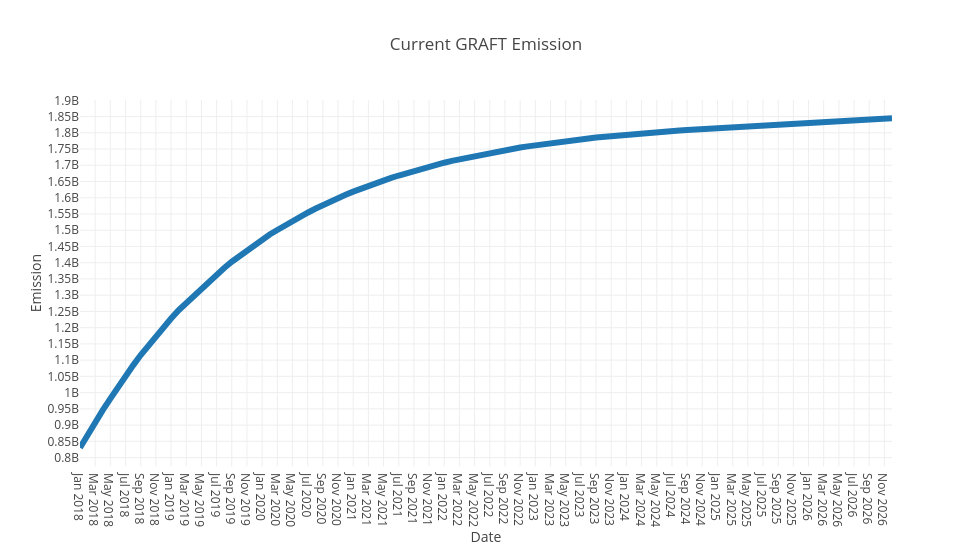
As you can see, the correction will not change the total maximum amount of GRAFT that will be ever created, it will just stretch the emission curve such that it will take longer to mine the total supply (see the existing and the new emission curves on the diagrams below).
All GRAFT supporters should benefit from the corrected emission formula because it is supposed to limit the daily increase in circulating supply, which will reduce the overall supply growth rate and stabilize the price. Long-term miners will benefit from the reduced emission for two reasons: 1) the price will go up so they will receive the same, or even better, revenue, and 2) the emission curve will be stretch, so they will get a more steady income over the extra years without the need to rely on transaction fees.
The emission reduction change requires a major network update (aka “hard fork”), which will be scheduled for block 176,000 (September 17, 2018). The major network update means that each GRAFT network node must be updated to the new software version before that block/date. Otherwise, the node that wasn’t updated is going to be on the wrong version of the blockchain. The new release will be available for download on September 10, 2018.
As another reminder, a major network update means that if you are running the GRAFT network node (graftnoded daemon), you must upgrade it to the current software release as soon as possible. If you do not install the updated node before the block 176,000, it will be disconnected from the mainnet after block 176,000.
Note that the users of mobile and desktop wallets will not be affected by the upcoming major network update and don’t need to do anything—as long as they are still connected to the default proxy supernodes (if you are connected to your own supernode, however, do not forget to upgrade the underlying network node to stay on the right network).