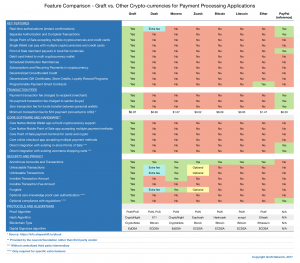
Our main goal is making the cryptocurrencies as convenient as plastic cards, while keeping the payment secure and private. We do this on both sides of the transaction: the buyer and the seller (merchant). In order to achieve those goals, we need a smooth transition from traditional payment methods, such as credit cards, to more progressive ones, like cryptocurrency. It is naive to believe that buyers and sellers will suddenly forget about plastic cards, which have a strong presence in the market and don’t go away anytime soon. Thus, Graft combines both methods and makes the payment process simple and available in any situation. The buyer can pay with their cryptocurrencies directly wherever it’s possible, but use the plastic card, which is linked to the wallet, in any other place that is not yet familiar with crypto. The same is with the seller. Using single point of sale app, merchant can accept various crypto-currencies and credit/debit cards.
In addition to these main goals, we are designing more services that will be provided by GRAFT network to improve the lives of sellers and buyers. For example, obtaining an instant credit by the buyer, or creating merchant tokens, which will be used by sellers as “private cryptocurrency” for important business functions such as store credits, loyalty rewards, gift certificates, and discount coupons.
There is another interesting and promising feature, which is in conjunction with merchant tokens elevates Graft from “another payment network” to a universal payment platform. This feature is called vchain, from the combination of words “virtual”, “chain”, and “blockchain”. Using vchain, sellers can connect several points of sale located in one store, or even create a network (“chain”) with multiple stores. Buyers can also use vchain to manage multiple wallets linked to each other and transfer funds for free between multiple accounts, which is useful for family or corporate accounts.
And finally, a few words about security and privacy. GRAFT uses the CryptoNote protocol, which is by far the highest achievement of modern cryptography. CryptoNote provides incomparably better privacy features comparing to any other blockchain protocol. Payments recorded on the GRAFT blockchain can not be viewed, traced, or linked to particular identity without consent. CryptoNote completely conceals from prying eyes almost all the attributes of the transaction: the buyer’s address, the amount of payment, and the address of the seller. On top of that, GRAFT adds another feature that is unique and has not yet been implemented by anyone else: hidden transaction fee amount. Thus, serious buyers and sellers, who really care about privacy of their financial transactions, for the first time have an opportunity to make their payments in cryptocurrency or cards without the risk of spying from competitors, criminals, or just random observers.